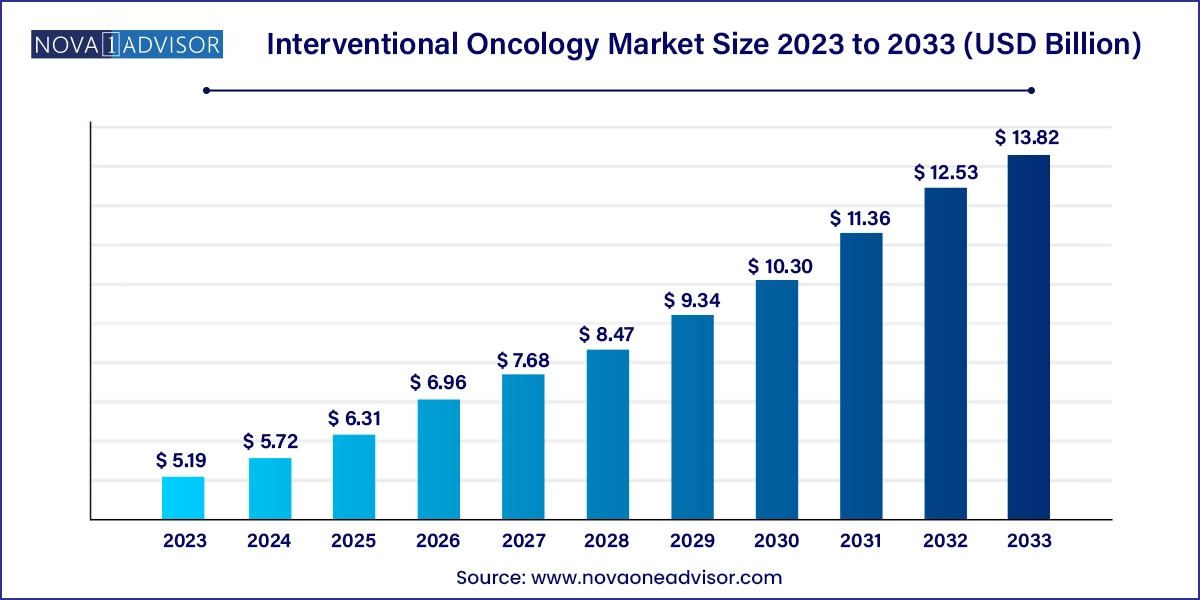
The global interventional oncology market size was valued at USD 5.19 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to reach around USD 13.82 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 10.29% from 2024 to 2033.
The Interventional Oncology (IO) Market represents a pivotal and rapidly expanding frontier in cancer care. Defined by minimally invasive, image-guided procedures for diagnosis and treatment, interventional oncology is transforming how solid tumors are managed across various organ systems. Unlike traditional systemic treatments or surgical approaches, IO techniques offer targeted, localized therapy that minimizes collateral damage, shortens recovery times, and often allows outpatient management. As cancer continues to be a leading cause of mortality globally, the demand for advanced, patient-friendly treatment modalities like IO is growing exponentially.
This market encompasses a diverse portfolio of technologies and procedures including tumor ablation, embolization therapies, biopsies, and targeted therapy delivery systems, all supported by image-guided techniques. Procedures such as radiofrequency ablation (RFA), microwave ablation (MWA), transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), and radioembolization are increasingly used in clinical settings to treat liver, lung, kidney, and other difficult-to-operate cancers.
Interventional oncology is also gaining traction due to its integration into multimodal cancer therapy regimens, where it complements surgery, radiotherapy, and systemic treatments such as immunotherapy. Innovations in nanomedicine, drug-eluting technologies, and precision imaging have further broadened the applicability and efficacy of IO procedures. Major players in the healthcare industry such as Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Terumo Corporation, and Siemens Healthineers are investing significantly in R&D, device innovation, and global expansion to capitalize on this growing domain.
Shift Toward Minimally Invasive Therapies: Patients and healthcare providers increasingly prefer IO over traditional surgery due to faster recovery, fewer complications, and outpatient feasibility.
Integration with Precision Oncology: IO techniques are being incorporated into personalized treatment plans, enabled by molecular imaging and AI-driven diagnostics.
Technological Convergence in Imaging and Therapy: Advances in real-time imaging such as cone-beam CT and MRI-guided interventions are enhancing procedural accuracy and outcomes.
Emergence of Drug-Eluting Technologies: Drug-eluting beads, stents, and hydrogels that deliver chemotherapeutics locally are gaining traction for their targeted delivery and reduced systemic toxicity.
Growth in Non-Hepatic Applications: While liver cancer remains the primary application, IO is expanding into lung, kidney, prostate, and breast cancers with tailored approaches.
Expanded Use in Palliative Care: IO techniques are increasingly used to manage cancer pain, hemorrhage, and obstructions, offering symptomatic relief in terminal stages.
Tele-guided and Robotic-assisted Procedures: The development of robotic catheters and remote procedure guidance is enabling interventional radiologists to perform complex IO remotely or with higher precision.
| Report Attribute | Details |
| Market Size in 2024 | USD 5.72 Billion |
| Market Size by 2033 | USD 13.82 Billion |
| Growth Rate From 2024 to 2033 | CAGR of 10.29% |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024 to 2033 |
| Segments Covered | Technique, procedure, application, end use, region |
| Market Analysis (Terms Used) | Value (US$ Million/Billion) or (Volume/Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Key Companies Profiled | Medtronic plc; Boston Scientific Corporation; Johnson & Johnson (Ethicon); Baxter International Inc.; Cook Medical; C.R. Bard Inc. (Acquired by BD); AngioDynamics Inc.; Stryker Corporation; B. Braun Melsungen AG; Terumo Corporation; Siemens Healthineers; GE Healthcare |
A central driver of the interventional oncology market is the surging global incidence of cancer, coupled with the clinical and economic advantages of localized, targeted therapies. According to the World Health Organization, cancer was responsible for approximately 10 million deaths in 2022, with liver, lung, breast, and colorectal cancers leading in prevalence and mortality. With the burden of cancer rising, healthcare systems are under pressure to deliver effective, resource-efficient treatment solutions.
Interventional oncology offers a promising answer. Techniques like transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) enable localized treatment with fewer side effects compared to systemic chemotherapy or radiotherapy. In liver cancer, for example, TACE has become a gold standard in managing intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Moreover, interventional oncology often provides a viable alternative to patients who are ineligible for surgery, expanding therapeutic access. The growing evidence base supporting IO procedures across cancer types has led to their inclusion in clinical guidelines, further propelling adoption.
Despite its clinical promise, the interventional oncology market faces a significant restraint in the form of high equipment costs and infrastructure requirements. Setting up an IO unit involves substantial investments in imaging equipment such as CT scanners, MRI systems, fluoroscopy, and angiography suites. These capital expenses, along with the cost of single-use devices like ablation probes, catheters, and embolization particles, can be prohibitive, particularly for hospitals in low-resource settings.
Moreover, interventional oncology procedures require specialized personnel including interventional radiologists, anesthesiologists, and nursing teams trained in image-guided techniques. This reliance on multidisciplinary expertise limits adoption in rural and underserved areas. Reimbursement challenges in certain countries and a lack of uniform clinical protocols also impede the broader implementation of IO. Without policy-level support and strategic investment in training and infrastructure, the full potential of interventional oncology may remain untapped in some regions.
One of the most promising opportunities lies in the convergence of interventional oncology with nanotechnology and advanced drug delivery systems. Innovations such as injectable hydrogels, nanoparticles, and drug-eluting beads are revolutionizing how therapeutics are delivered to tumors. These materials can be engineered to release drugs in a controlled manner at the tumor site, enhancing efficacy and minimizing systemic side effects.
In parallel, advances in imaging techniques—such as MRI thermometry and contrast-enhanced ultrasound—are making it possible to monitor therapy in real time. Companies are developing dual-function agents that serve both as imaging contrast and therapeutic vehicles. For instance, magnetothermal nanoparticles can be guided magnetically and activated through external fields to ablate tumors. These technologies not only promise higher treatment precision but also open the door to treating previously inaccessible or high-risk tumors with minimal invasiveness. The ongoing clinical trials and partnerships between pharma and medtech firms are expected to accelerate the commercialization of these cutting-edge innovations.
Ablation therapies dominate the technique segment, led by radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA). These methods are especially effective for treating liver, lung, and renal tumors, offering a non-surgical, repeatable, and often outpatient treatment. RFA, for example, uses high-frequency alternating current to induce thermal destruction of cancer cells. It is widely accepted for treating hepatocellular carcinoma in patients who are poor surgical candidates. MWA, with its deeper penetration and faster heating, is gaining favor for larger or more vascular tumors.
Targeted therapy delivery systems are the fastest-growing segment, especially drug-eluting beads and hydrogels. These innovations enable highly localized delivery of chemotherapy or radiopharmaceuticals, reducing systemic toxicity. Transarterial radioembolization (TARE) with yttrium-90 microspheres has shown promising results in liver cancer. The development of injectable nanoparticles that combine diagnostic and therapeutic functions is also spurring interest, particularly in precision oncology and clinical trials.
Tumor ablation is the most widely used procedure, thanks to its growing success in managing both primary and metastatic tumors. Thermal ablation using RFA or MWA is often the first choice for small tumors and can be used in conjunction with systemic therapies. Its growing adoption is also due to its cost-effectiveness and fewer hospital admissions.
Vascular interventions are growing rapidly, primarily because of their use in embolization therapies like TACE and TARE. These procedures are often performed in interventional radiology labs and are being expanded to treat tumors in the pancreas, uterus, and bones. Palliative care procedures, such as neurolytic blocks for pain or embolization for bleeding, are also gaining attention as cancer survivorship and life expectancy improve.
Liver cancer remains the largest application segment, as IO techniques like TACE and RFA are considered mainstays in treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), particularly in Asia and Africa where the disease is endemic. In high-income countries, these treatments serve patients who are not candidates for surgery or transplantation.
Lung cancer is the fastest-growing application, particularly for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). IO procedures are increasingly used in patients who are not eligible for lobectomy or stereotactic body radiation therapy. Cryoablation and MWA are being applied in both primary and metastatic lung tumors, with ongoing research showing comparable outcomes to traditional surgery in select cohorts.
Hospitals dominate the end-use segment, largely due to the infrastructure and multidisciplinary expertise required for IO procedures. Comprehensive cancer centers often house interventional radiology suites equipped for advanced ablation, embolization, and targeted therapy procedures.
Specialty clinics are the fastest-growing setting, particularly in urban regions of developed markets. These centers focus on outpatient interventional treatments, often affiliated with larger hospitals or research institutions. The convenience and cost benefits of outpatient IO are driving expansion in this segment, along with a focus on patient-centered care.
North America dominates the interventional oncology market, driven by its strong healthcare infrastructure, technological advancements, and high cancer prevalence. The U.S. accounts for a large share of global IO procedures, supported by widespread availability of interventional radiologists and reimbursement for ablation and embolization treatments. Leading hospitals such as MD Anderson Cancer Center, Mayo Clinic, and Cleveland Clinic are known for their advanced IO programs. The region also hosts numerous clinical trials testing novel IO technologies, from radioembolization to image-guided drug delivery systems.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing market, fueled by rising cancer incidence, improved healthcare access, and rapid infrastructure development. Countries like China, India, South Korea, and Japan are investing in modernizing oncology care, and IO is gaining momentum as a cost-effective, less invasive treatment alternative. China has become a major hub for liver cancer treatment using TACE and MWA, while Japan leads in high-precision imaging techniques. As awareness grows and reimbursement systems evolve, the adoption of interventional oncology is expected to surge across this region.
In March 2025, Boston Scientific announced FDA clearance for its MicraFlex Ablation Catheter, offering enhanced flexibility and performance in liver and lung tumor ablations.
Medtronic, in February 2025, launched a new generation of radiofrequency ablation generators with integrated AI analytics for real-time tissue feedback, optimizing safety and efficacy.
Terumo Corporation expanded its drug-eluting bead platform in January 2025, targeting Europe and Asia for new indications beyond liver cancer, including kidney and breast tumors.
In December 2024, Siemens Healthineers partnered with Philips to develop a co-branded MRI-guided ablation system, merging Siemens’ imaging expertise with Philips’ interventional suite capabilities.
BTG International, a subsidiary of Boston Scientific, initiated a multi-center clinical trial in November 2024 to assess the use of microspheres in combination with checkpoint inhibitors for liver cancer immunotherapy
This report forecasts revenue growth at country levels and provides an analysis of the latest industry trends in each of the sub-segments from 2021 to 2033. For this study, Nova one advisor, Inc. has segmented the Interventional Oncology market.
By Technique
By Procedure
By Application
By End Use
By Region